Google will no longer phase out third-party cookies on Chrome, as has been continually announced since 2020.
Yes, it’s a shock to us all. But at the same time, is it?
This article covers everything worth knowing about third-party cookies, Google’s decision, and how it will impact users and advertisers moving forward.
Key Highlights on Google’s Third-Party Cookie Phase-Out Delay
- Google delayed the phase-out of third-party cookies until 2025, allowing advertisers more time to adjust and develop new strategies.
- This delay supports the continued testing of Privacy Sandbox alternatives, which aim to balance privacy and advertising needs.
- New Chrome privacy controls offer users better data management and the ability to disable ad tracking features.
- The shift emphasizes first-party data collection as a sustainable strategy.
- Advertisers are encouraged to adopt contextual targeting and strengthen publisher partnerships to offset future impacts.
TABLE OF CONTENTS:
What Are Third-Party Cookies?
Third-party cookies are tracking codes placed on a website visitor’s computer by a website other than the one they are currently visiting. These cookies are commonly used for advertising and tracking purposes, allowing advertisers to track user behavior across multiple websites.
This data is crucial for targeted advertising and understanding consumer preferences. These cookies enable features like retargeting ads and personalized marketing, but have raised concerns regarding privacy and data protection. As the digital landscape evolves, there’s a growing emphasis on privacy, leading to changes in how third-party cookies are used and regulated.

In other words, Google’s decision to phase out these cookies marked a significant shift towards enhancing user privacy.
The phase-out presented challenges for marketers who rely heavily on third-party data. The inability to track user behavior across sites would lead to less effective targeting and a potential decrease in advertising revenue.
However, it also offers an opportunity to innovate and find new ways of engaging with customers (more on strategies below).
Google’s Reversal on Third-Party Cookie Deprecation
To the surprise of many, Google announced in July 2024 that it was changing its plans to phase out third-party cookies in Chrome.
For over four years, Google has been working toward eliminating these cookies. The goal was to enhance user privacy by deprecating third-party cookies and replacing them with the Privacy Sandbox, which would allow websites to access user data without invading their privacy or using tracking cookies.
That’s no longer the case.
This dramatic pivot by Google is due largely to the complex process of developing and testing alternative technologies that can balance privacy needs and advertisers’ requirements.

Google’s decision to postpone the removal of third-party cookies stems from regulators’ and advertisers’ worries. As Google’s primary revenue generators, advertisers expressed concern that eliminating cookies from Chrome would restrict their capacity to gather data for ad personalization.
Many didn’t even believe Google would actually go through with it; per Forrester in its Marketing Survey for 2024, 61% of marketers didn’t think Google would deprecate third-party cookies.
Google also faced pushback from regulators for its Privacy Sandbox initiative, particularly the UK’s Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) and the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO). Some issues raised include:
- Anticompetitive concerns: Google’s sole control over Privacy Sandbox allows them to unilaterally adjust its operations and data availability, potentially impacting the entire global advertising ecosystem.
- Insufficient privacy disclosures: Regulators worry that explanations of Privacy Sandbox and Topics API aren’t clear enough to educate the average consumer on how their data is collected and used. Even now, cookie banners struggle to effectively communicate the nature and purpose of cookies, as well as their data collection practices, to the average user.
- Fingerprinting risks with Topics: Research shows that knowing just four data points about users’ most visited websites is enough to identify 95% of individuals. There are also concerns about widespread access to users’ Topics and the potential for drawing broader inferences from these lists.
While marketers may breathe a sigh of relief (for now), privacy advocates are not happy. Lena Cohen, a staff technologist at the Electronic Frontier Foundation, argues that cookies can lead to consumer harm by enabling predatory advertisers, such as payday lenders, to target vulnerable groups like those struggling with money issues.
“Google’s decision to continue allowing third-party cookies, despite overwhelming evidence of their surveillance harms, is a direct consequence of their advertising-driven business model,” Cohen said in a statement.
However, Google isn’t ditching the idea of user agency and privacy control entirely. The last few years of focused testing and troubleshooting has led to some interesting developments that Chrome users will have access to.
What Is Google’s Privacy Sandbox Initiative?
Google has been working on the Privacy Sandbox initiative since 2019 with the goal of enhancing online privacy while supporting digital businesses as we move toward a cookieless future. The Privacy Sandbox aims to reduce cross-site and cross-app tracking while maintaining free access to online content and services.
At its core, Google’s Privacy Sandbox initiative encompasses the following key elements:
- Shifting data processing and ad targeting to the local browser environment
- Phasing out support for third-party cookies in Chrome
- Introducing new APIs for privacy-preserving alternatives to common web use cases
- Providing users with more control over their data and online privacy
- Developing open standards for these new technologies in collaboration with the web community
The July 2024 decision to stop phasing out third-party cookies won’t impact Privacy Sandbox. Anthony Chavez, VP of the Google-backed Privacy Sandbox initiative, said:
“Instead of deprecating third-party cookies, we would introduce a new experience in Chrome that lets people make an informed choice that applies across their web browsing, and they’d be able to adjust that choice at any time . . . We’ll continue to make the Privacy Sandbox APIs available and invest in them to further improve privacy and utility.”
Google ran tests on its Privacy Sandbox tech during Q1 of 2024, and the results looked promising. They wanted to figure out how advertisers’ revenue might change if third-party cookies went away.
To do this, they looked at the numbers for both Ad Manager and AdSense users without third-party cookies and compared those results to a scenario where Privacy Sandbox was available as an alternative.
The results showed that removing third-party cookies on their own would cause a 34% drop in programmatic revenue for advertisers using Google Ad Manager and a 21% drop for AdSense.
When Google turned on the Privacy Sandbox features, they saw a smaller hit to revenues; Ad Manager users experienced a drop of about 20%, while AdSense publishers saw their earnings decrease by roughly 18%.
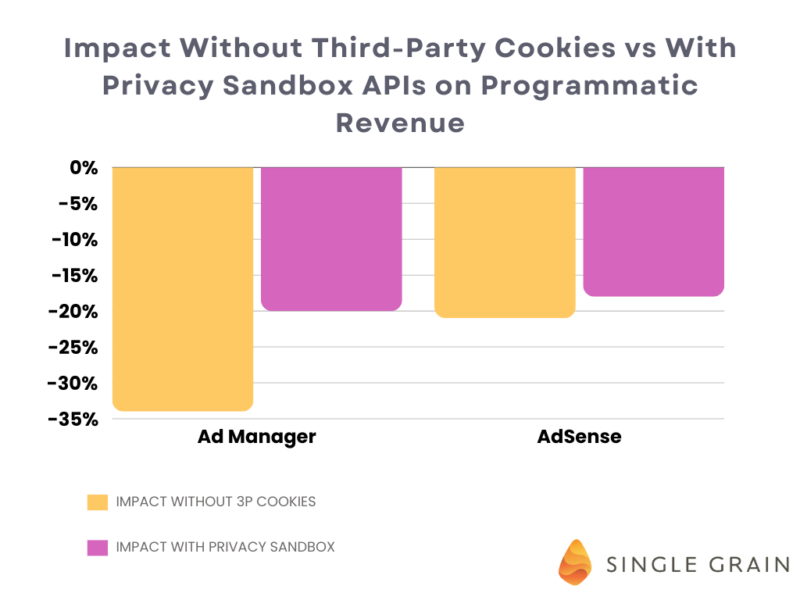
This might seem like a huge drop (and it is!) but Google’s proposition seems to be that in a cookieless future caused by default cookie-blocking in browsers like Firefox and Safari as well as users’ own privacy choices, it’s better to have Privacy Sandbox than not have it.
With this in mind, the decision to continue developing Privacy Sandbox APIs as potential alternatives makes sense. These APIs aim to reduce cross-site tracking while maintaining the functionality needed for free online services, including support for third-party apps.
There are over 30 proposals under the Privacy Sandbox, each covering various use cases and requirements. For example, the Topics API supports interest-based advertising and content personalization without third-party cookies.
Similarly, the Protected Audience API allows for remarketing and creating custom audiences:
Need help adapting to Google’s Privacy Sandbox? Single Grain’s marketing experts can help!👇
New Privacy Control Options for Chrome Users
Google announced new settings within Chrome that make it easier for website users to manage their privacy preferences across their web browsing activities. The new privacy control options put you in charge of your online privacy.
One of the standout features is the ability to disable the Privacy Sandbox by adjusting three specific settings in a user’s Chrome browser.
- Your choice of ad content: You can now control ‘Ad topics,’ which allows Google to generate a list of interests based on your browsing history.
- Control of suggested ad content: There’s also the ‘Site-suggested ads’ setting, which enables remarketing by allowing sites to share data with Chrome for targeted advertising, including Google ads.
- User interface options: Chrome users will see a new privacy-related screen offering options like ‘Settings’ and ‘Got It’. This user-friendly interface, incorporating Google consent mode, is designed to help you make informed choices about your privacy settings rather than just defaulting to less protective options. It’s all about giving you the power to decide how your data is used.
These three new controls basically give website users the power to control what data Google collects to inform its algorithm on your specific preferences.
For some, this might be considered not enough privacy restraint, while for others, it will be much more preferable over the options they’ve had up until now (which are very few).
User Choice and Control Over Web Browsing Privacy
Google’s revamped approach to privacy puts user choice at the forefront. Instead of just blocking third-party cookies entirely, Google is giving website users the ability to make informed choices about their online privacy.
Whether users like it or not, they will continue to be served advertisements across Google’s network and apps.
So, the decision is now in their hands to decide whether or not those ads will be tailored to their observed needs and preferences or if they’re a little more unpredictable.
This experience is a touch similar to what we’ve seen with Apple’s App Tracking Transparency, which resulted in significant reductions in tracking acceptance:
Now, Chrome users can expect a privacy framework that respects their preferences and offers clear options. If you want to take charge of your privacy, you can navigate to your Chrome browser account settings and select “My Ad Center“:
From there, you can set all of your preferences related to how Google collects your data and serves your ad content.
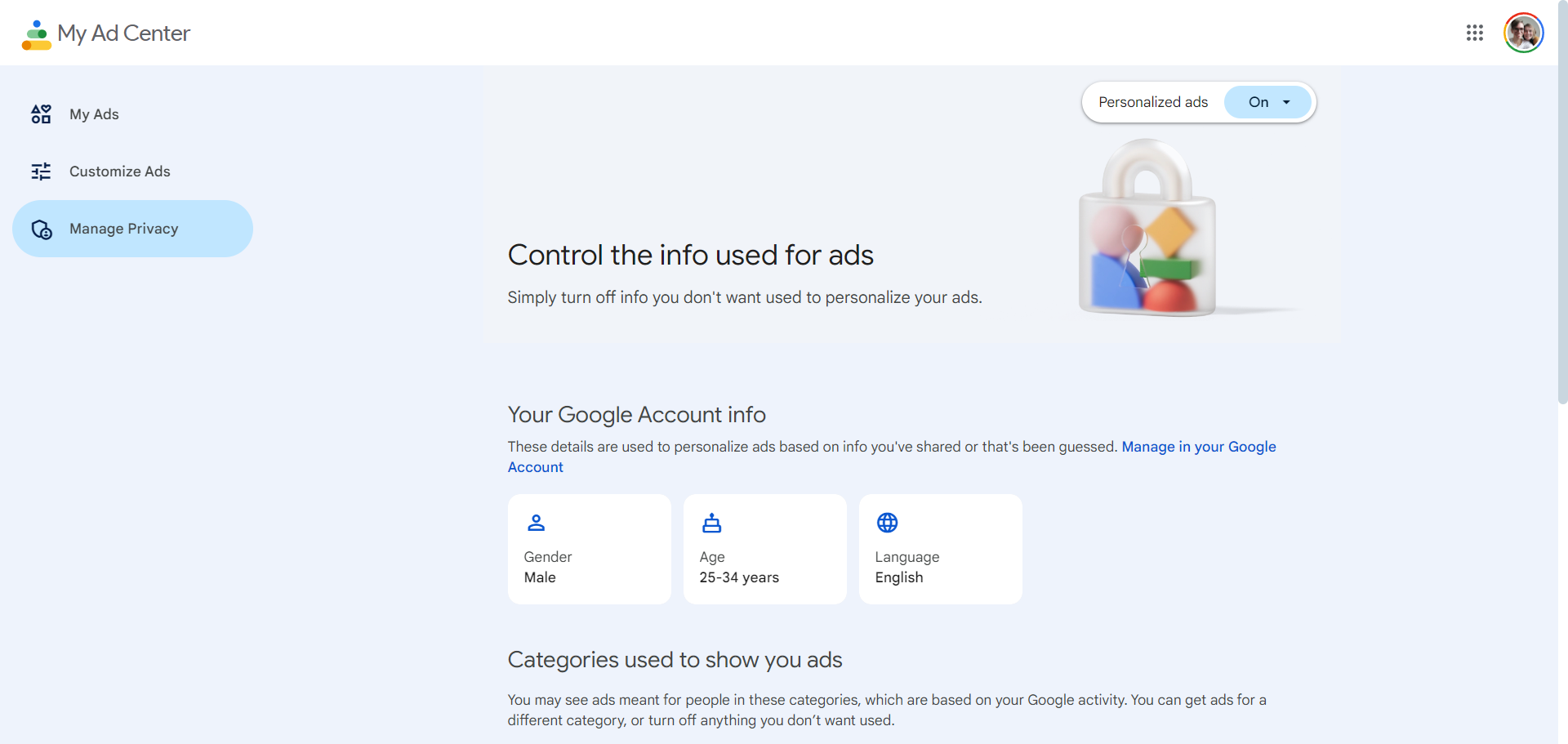
These new options are designed to give website users control over their web browsing privacy, ensuring that you have the tools to protect your personal data points while navigating the web.
Whether it’s through the address bar or deeper in the settings, you’ll have the power to decide what gets tracked and what doesn’t.
Implications for Advertisers and Publishers
Advertisers and publishers will no doubt appreciate Google’s decision to keep third-party cookies even in a modified capacity. After all, it’s these tracking cookies that lend stability and predictability to their marketing tactics.
Third-party cookies have been crucial for targeting and measuring ad performance over the past decade, and their removal would have required significant adjustments in how advertisers operate.
However, despite the decision to stop phasing out third-party cookies, marketers still face challenges. 3P cookies are going to go extinct whether we like it or not. With that in mind, advertisers should consider these strategies:
- Expand testing efforts: Explore alternative targeting methods such as contextual approaches, innovative creative content, and various identity resolution techniques. Remember that a substantial portion of users already browse in “cookieless” environments, whether through privacy-focused browsers or Chrome extensions. While Google’s announcement may have reduced urgency, the need for adaptation remains critical.
- Enhance data strategies: Determine the essential consumer data required for creating look-alike models, segments, and propensity scores. Develop a plan to acquire this information ethically. A robust data strategy will prove invaluable when considering data clean room partnerships, ensuring that such collaborations align with specific use cases and business goals.
- Strengthen publisher relationships and prioritize direct buying: Third-party cookies were never the sole means of understanding customers. Publishers possess valuable insights about their audiences, including device usage, browser preferences, and opt-in choices. By leveraging seller-defined audiences, internal modeling capabilities, and supply-side platforms that facilitate relevant identity token transactions, publishers are well-positioned to assist advertisers in navigating the post-third-party cookie landscape.
The end of third-party cookies marks a major change in digital advertising. Advertisers and marketers need to rethink their approaches in this new environment and shift to different targeting techniques, focusing more on collecting first-party data from direct customer engagement:
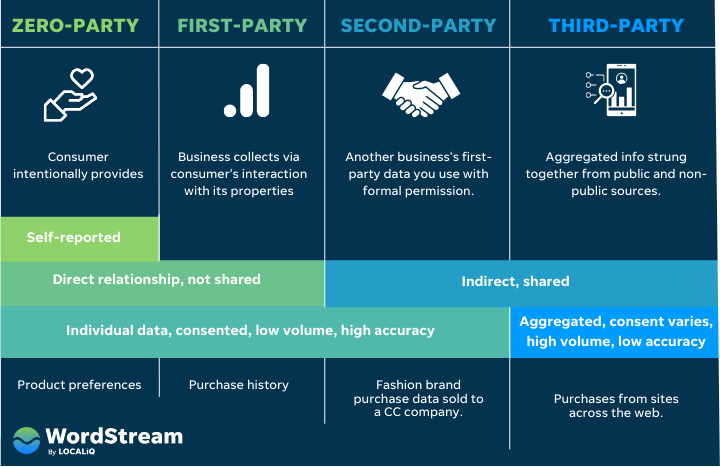
First-party data includes information derived from user interactions with the website, products, or services. Examples include data from website analytics (like page views or session duration), customer purchase history, or information provided through forms and surveys.
This data is valuable for businesses not only because it is specific to their audience, but also because it’s more reliable and privacy-compliant — in other words, it offers insights without compromising user trust.
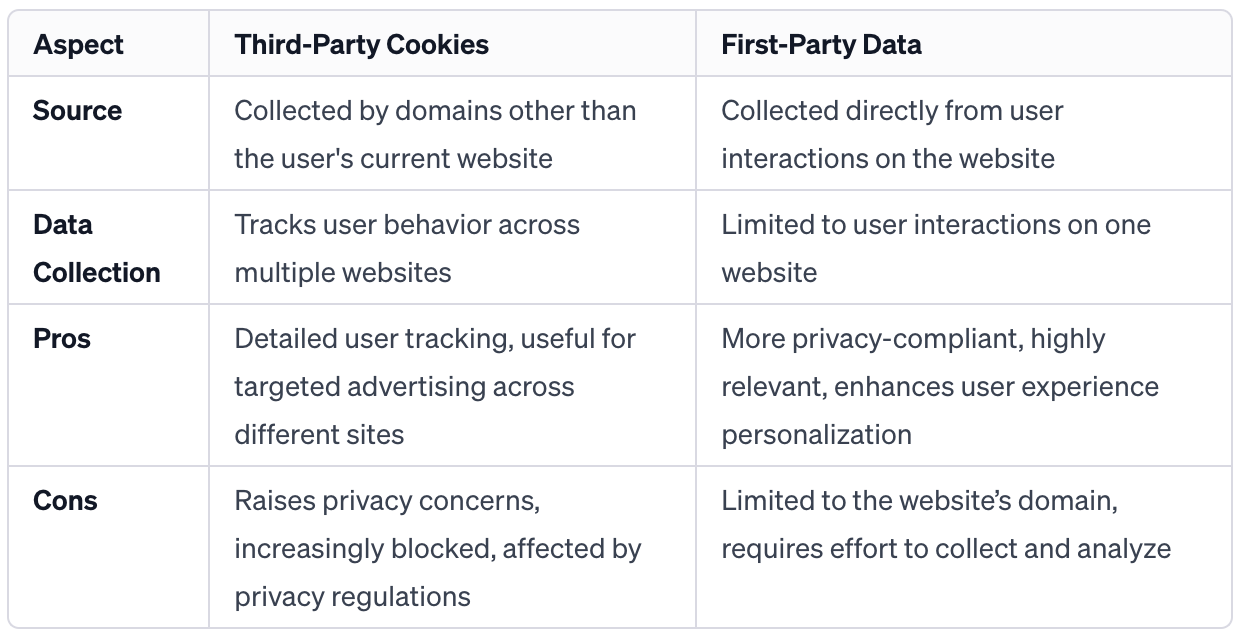
Strategies for Leveraging First-Party Data
Leveraging first-party data involves using the data collected directly from your audience or customers through interactions with your business. This data is valuable as it’s more accurate, relevant and under your control.
Here are some effective strategies for leveraging first-party data:
- Personalization: Use the data to personalize the customer experience. This can include customizing marketing messages, product recommendations, and content based on the user’s previous interactions and preferences.
- Customer segmentation: Segment your audience based on their behavior, interests, or demographic information. This allows for more targeted and effective marketing campaigns.
- Predictive analytics: Apply predictive analytics to your first-party data to predict future behaviors and trends. This can help in forecasting sales, identifying potential high-value customers, or understanding which products might be most appealing to certain segments.
- Enhanced customer service: Use the data to improve customer service. Understanding customer history and preferences can help in providing more efficient and personalized support.
- Product development: Leverage the insights gained from the data to inform product development. This can lead to creating products or features that better meet the needs of your customers.
- Optimizing user experience: Create compelling and interactive content (like quizzes or polls) that encourage users to engage directly with your site. Analyze the data to understand how customers interact with your website or app and use these insights to optimize the user experience, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
- Compliance and privacy: Ensure that you’re compliant with data privacy laws like GDPR or CPRA. Being transparent about how you collect and use data can also help in building trust with your customers.
- Cross-channel marketing: Use first-party cookies to create a consistent marketing experience across various channels, whether it be email, social media, or your website.
- Retention strategies: Analyze customer lifecycle and engagement to develop strategies for customer retention. Tailor offers and communications to keep your existing customers engaged.
- Feedback loop: Use the data to create a feedback loop where customer responses and interactions help in continually refining and improving your strategies.
Remember, the goal is to enhance the customer experience and build a stronger relationship with your audience while respecting their privacy.
The bottom line: a world without third-party cookies requires advertisers and marketers to completely rethink how they get, manage, and use data.
Counterpoint: Does Third-Party Cookie Deprecation Even Matter Anymore?
As the digital advertising industry prepares for the loss of third-party cookies, a crucial question emerges: Does this change even matter?
The landscape of online marketing has already shifted dramatically, with clicks and attribution losing their once-paramount importance. This evolution suggests that the impact of cookie deprecation might be less dramatic than initially feared.
The Decline of Click-Based Tracking and Attribution
The backbone of digital advertising — click-based tracking and attribution — has been eroding for years. This shift is driven by several factors:
- Multi-device journeys: Tracking users across multiple devices has become nearly impossible, even with advanced techniques like browser fingerprinting.
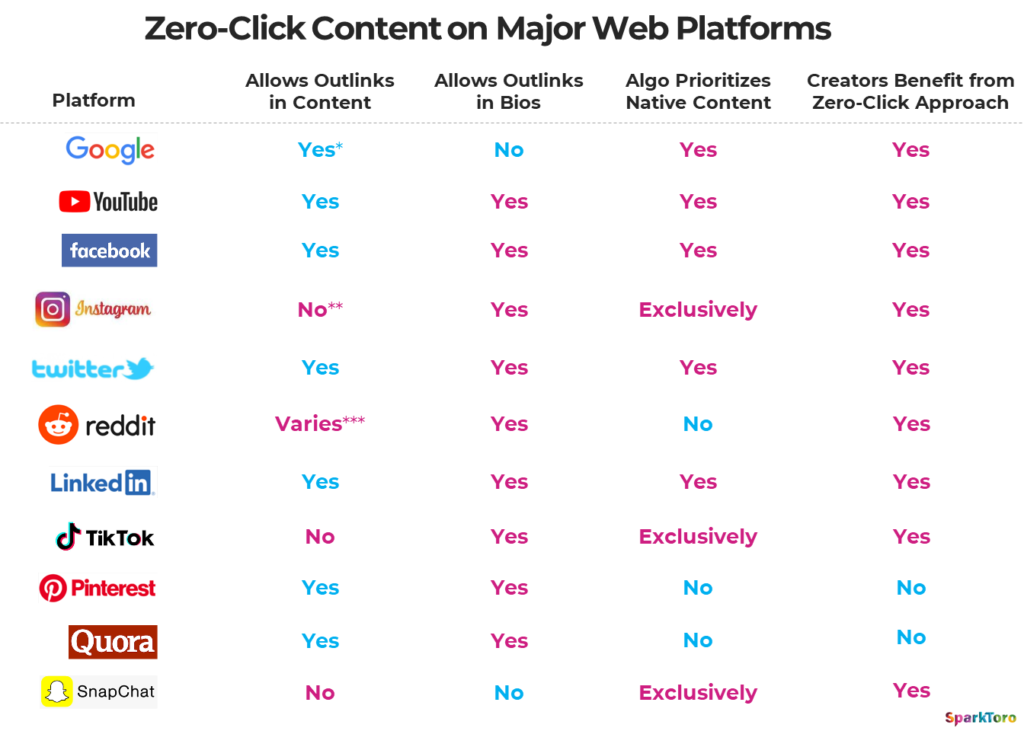
- The “zero click problem”: Internet users have collectively stopped clicking as frequently as they used to, partly due to platforms training us to consume content natively. YouTube wants us to stay on YouTube, as does LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and so on:
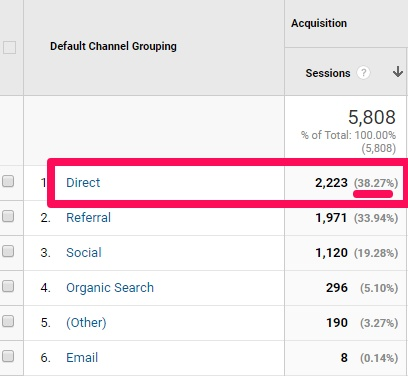
- Dark traffic: A lot of traffic lacks referral information, making it difficult or impossible for analytics tools to determine their source. Many major social networks now hide some or all of their referral data, which further complicates attribution efforts. For instance, direct traffic is usually around 20% of your site’s total traffic, but in the image below, it’s almost twice as much at 38%; that discrepancy is caused by dark traffic:
These changes have been happening regardless of cookie status, indicating that the industry was already moving away from traditional tracking methods.
The digital landscape has also become more fragmented and privacy-focused, further complicating tracking efforts and killing attribution. We now have to deal with:
- Ad blockers: An increasing number of internet users are using ad blockers (estimates vary from 30% to 50%), and these tools are not only blocking ads but also preventing various forms of tracking.
- In-app activity: The dominance of mobile apps creates data silos, with only major platforms like Google, Apple, and Meta having comprehensive cross-platform insights.
- Cookie permissions and do-not-track protocols: These have now rolled out globally on almost all the major browsers, limiting data collections.
- Legal restrictions: From GDPR in the EU to CPRA in California and anti-tracking and privacy laws in Canada, Brazil, and other places, user tracking is quickly becoming illegal or heavily regulated in many parts of the world.
A paradox also exists in the realm of search engines. As Rand Fishkin, cofounder of SparkToro noted, while search engines account for a majority of website referrals, users spend only a fraction of their online time on these platforms:

Search engines like Google and Bing account for upwards of 70% of all traffic referrals; however, search engines only accounted for 10% of all visits by users:

This discrepancy points to the influence of other digital spaces on search behavior, although these influences often go uncredited in traditional attribution models.
In light of these changes, new marketing approaches are gaining traction. There’s a growing emphasis on understanding the sources of influence for target audiences, rather than relying solely on direct click data.
Marketers are recognizing the importance of multiple touchpoints in the customer journey, many of which don’t leave easily trackable data. The focus is shifting toward maintaining visibility in spaces where the audience spends time, even when the impact of these efforts can’t be directly linked to sales.
As we move into a post-cookie era, the industry is seeing a necessary shift towards more holistic, influence-based marketing strategies. Success in this new landscape will hinge on a deep understanding of audience behaviors, identification of key influence sources, and the ability to measure success through overall market lift rather than direct attribution.
While this approach presents challenges in quantification, it has the potential to yield more effective and resonant marketing efforts.
So, while the deprecation of third-party cookies represents a significant change, the digital marketing world has already been adapting to a more complex, less directly attributable environment.
The future of marketing lies not in lamenting the loss of cookies, but in embracing a more nuanced, multi-channel approach that reflects the true complexity of consumer behavior in the digital age.
Last Words on Google Third-Party Cookies Phaseout Getting Dropped
Google’s reversal of third-party cookie deprecation marks a major pivot in their alleged advocacy for user privacy. They haven’t abandoned the initiative to create a more wholesome and protected online environment.
However, they clearly bit off more than they could chew by promising a zero-cookie online world before they had the technical solution in place for advertisers.
With new privacy control options in Chrome and the continued development of the Privacy Sandbox, website users can expect more control over their online privacy.
Advertisers and publishers, meanwhile, will need to adapt to these changes and explore new strategies for engaging with their audiences.
Key Takeaways
- Google is delaying the phase-out of third-party cookies in Chrome until early 2025 to develop more effective privacy alternatives and address competition concerns.
- New privacy control options in Chrome give users better control over how their data is used, including features to disable the Privacy Sandbox and manage ad-related settings.
- Google’s Privacy Sandbox initiative aims to balance user privacy with the needs of the web ecosystem, featuring privacy-preserving APIs as alternatives to third-party cookies.
As we move toward a more privacy-conscious web, it’s crucial for everyone — from everyday web users to industry giants — to stay informed and proactive about privacy settings.
The future of web browsing is one where user choice and privacy are at the forefront, ensuring a safer and more transparent online experience for all.
If you’re ready to start strategizing with Google’s new privacy experience, Single Grain’s marketing experts can help!👇
Recommended Video
For more insights and lessons about marketing, check out our Marketing School podcast on YouTube.